Ezeepay Explains: Historic “Next-Gen” GST Overhaul—A Diwali Gift for India
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India has just seen its biggest shake-up since it first started. During the 56th GST Council meeting on September 3, 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled a major reform aimed at simplifying the tax framework, lowering rates on essential goods, and making it easier for businesses to comply.
This groundbreaking move—dubbed the Next-Gen GST Reform—is being introduced right before the festive season, making it a perfect “Diwali gift” for families, farmers, businesses, and industries across the board.
What’s New in GST?
Simplified Slabs
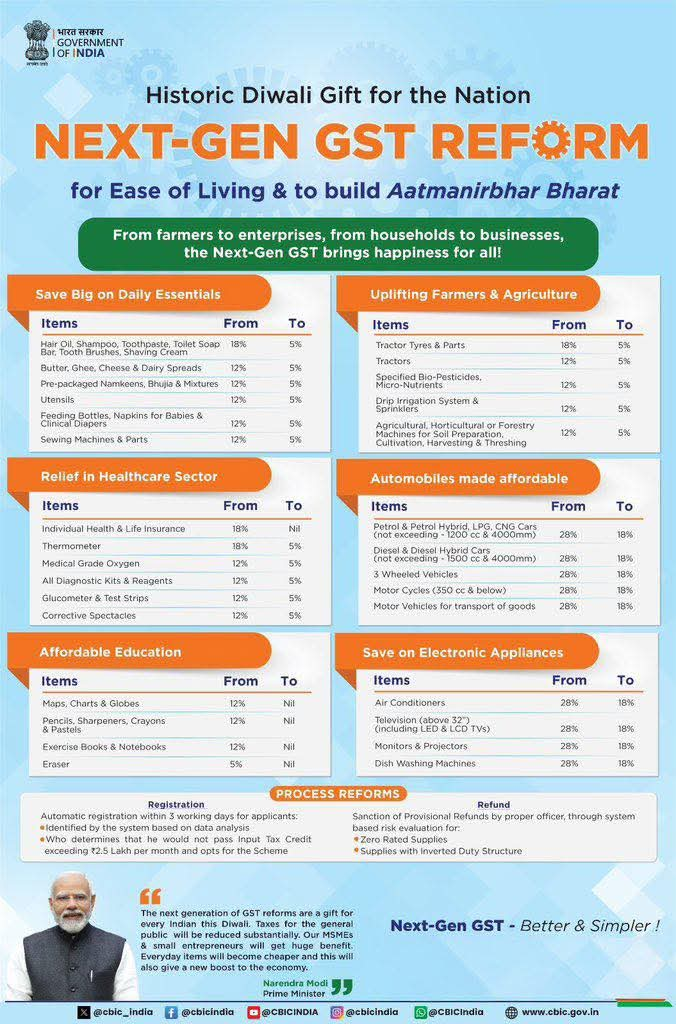
The previous four-tier GST system—5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%—has been simplified down to just two rates: 5% and 18%. Plus, there’s now a special 40% rate for luxury and sin goods.
Essentials Become Cheaper
A lot of everyday products have either dropped to the 5% tax rate or are now completely tax-free. For example, items like UHT milk, paneer, Indian breads, hair oil, soap, toothpaste, dairy spreads, and packaged snacks are now either in the 5% category or exempt from tax altogether.
Boost for Farmers and Agriculture
Farm equipment like tractors, drip irrigation systems, and soil preparation tools now only face a 5% GST. Even bio-pesticides and micronutrients have been moved to lower tax brackets, which helps cut down costs for farmers.
Healthcare Relief
Life-saving medications, oxygen cylinders, diagnostic kits, and even personal health and life insurance policies are now either tax-exempt or taxed at just 5%. This change is expected to lower healthcare costs and make services more accessible.
Affordable Education
Items such as notebooks, exercise books, charts, pencils, crayons, and globes are now exempt from GST, making educational materials more budget-friendly for students.
Electronics & Automobiles
On the consumer front, air conditioners, TVs, dishwashers, projectors, and monitors have seen a reduction in tax from 28% to 18%. In the automotive sector, small cars, motorcycles, buses, and trucks have also been moved to the 18% category, which is expected to make them more affordable and boost demand.
Luxury & Sin Goods
A new 40% tax bracket has been introduced for items like pan masala, tobacco, fizzy drinks, casinos, betting services, and luxury cars. This move aims to protect government revenue while also discouraging the consumption of harmful products.
Process Reforms
- Automatic Registration: Businesses will receive GST registration within 3 working days.
- Refunds: Refunds will be processed automatically via a system-based risk evaluation.
- Compliance Ease: MSMEs with input tax credit claims below ₹2.5 lakh per month can now opt for a simplified scheme.
Benefits of the Next-Gen GST
-
Relief for Households
As essentials become more affordable or even tax-free, middle-class and lower-income families will find themselves saving more each month. This extra cash means they’ll have more disposable income, which in turn boosts overall spending.
-
Boost for FMCG Sector
The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods sector, which relies heavily on volume sales, stands to gain from lower prices and a surge in demand. Companies are expected to pass on the benefits of tax cuts to consumers, which will further drive their sales.
-
Stronger Agricultural Base
With reduced costs for farm machinery and inputs, farmers are likely to enjoy better profits. This change also encourages the use of modern techniques, like drip irrigation, which can significantly enhance agricultural productivity.
-
Healthcare Accessibility
A lower GST on medicines, medical devices, and insurance will lead to less out-of-pocket spending for families. This is likely to increase insurance coverage, bolstering the financial security of citizens.
-
Educational Support
When we exempt stationery and educational aids, it lightens the financial load for both students and parents. This move is in line with the government’s long-term vision of fostering literacy and skill development.
-
Automobiles and Electronics Demand Surge
With price cuts on cars, bikes, and consumer electronics, we can expect a significant uptick in demand this festive season. This is a much-needed lifeline for industries that have been struggling with low demand in recent years.
-
Simplification for Businesses
Switching to just two tax slabs helps clear up confusion and reduces disputes over classifications. This change will particularly benefit small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), allowing them to navigate compliance with less hassle, saving them both time and money.
-
Economic Growth
With lower costs and increased demand in crucial sectors, we can expect a positive impact on GDP growth. Economists predict that this reform could add between 0.2% and 0.3% to India’s growth in the upcoming fiscal year.
Drawbacks and Challenges
-
Revenue Loss for Government
By cutting GST rates on essential goods and simplifying the tax structure, the government may face a significant revenue shortfall—estimated to be around ₹48,000 crore each year.
-
Pressure on State Finances
States that rely heavily on GST revenues might find themselves in a tough spot financially. It’s crucial to manage compensation mechanisms carefully to prevent budget gaps from widening.
-
Luxury & Sin Sector Hit
Industries tied to casinos, gambling, and luxury items are expected to take a hit. The hefty 40% tax rate could lead to a drop in investment, job opportunities, and tourism revenue, particularly in places like Goa and Sikkim.
-
Implementation Hurdles
Rolling out this new structure across the entire economy in just a few weeks could prove to be quite a challenge. Businesses will have to quickly update their billing systems, software, and processes.
-
Partial Relief Only
While there have been reductions for essentials and mid-range goods, not every industry has benefited. Some sectors are calling for a more thorough reform to help sustain growth in consumption.
Sector-Wise Impact
| Sector | Positive Effects | Challenges |
| Households | Lower monthly bills, more disposable income | Rising expectations for further tax relief |
| FMCG & Dairy | Higher demand, price cuts up to 10% | Lower margins may pressure companies |
| Agriculture | Cheaper inputs, improved productivity | Implementation delays in rural areas |
| Healthcare | Affordable medicines and insurance access | Sustainability concerns for insurers |
| Education | Reduced costs for parents and students | None significant |
| Automobiles | Increased demand for small cars, bikes, and commercial vehicles | Luxury car market could shrink |
| Electronics | Festive demand likely to spike for TVs, ACs, dishwashers | Global supply chain challenges may limit benefits |
| Luxury/Sin Goods | Revenue protection for govt, discouragement of harmful habits | Job losses, reduced investment in related sectors |
| States | Simplified tax regime, better compliance | Revenue loss concerns |
Final Thoughts
The Next-Gen GST Reform stands out as one of the most ambitious economic initiatives we’ve seen in recent years. It aims to streamline India’s tax system, lower living costs, support farmers, and make healthcare and education more accessible. Plus, it’s set to stimulate demand in key sectors like FMCG, automobiles, and electronics. For families, this reform translates to real savings. For businesses, it means easier compliance and new market opportunities.
And for the economy as a whole, it could signal the start of a growth cycle driven by consumer spending. That said, the success of this reform hinges on how well it’s put into action and how the government tackles any revenue shortfalls, particularly for the states. If handled properly, this reform could become a key part of India’s path toward a better quality of life and a self-reliant Bharat.